Definition: The condition in which people have insufficient, or no money or means of support to survive on.

Half the world’s population, almost three billion people, are forced to live on less than US$2 a day and over one billion of these live in extreme poverty. There are different types of poverty in the world, defined as:
Extreme (or absolute) Poverty:
Living on less than $1 a day, which means they are not able to afford the most basic necessities. Eight million people die each year from extreme poverty.
Moderate Poverty:
Living on around $1 - $2 a day which enables households to barely meet their basic needs but still forego many other things, such as education, healthcare etc.
Relative Poverty:
Living on an income slightly below the national average.
Poverty has a devastating effect on the lives of individuals, families and communities. Many never emerge from the cycle of poverty, causing their descendants to continue struggling within its grasps.
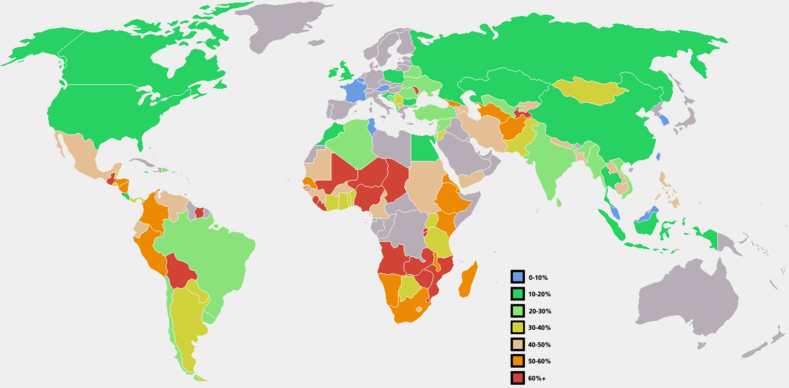
Key:
Blue = 0-10%
Dark Green = 10-20%
Light Green = 20-30%
Yellow = 30-40%
Peach = 40-50%
Orange = 50-60%
Red = 60-70%
The Main Causes of Poverty
There are many inter-related factors contributing to the existence of poverty, including:
· Little, or no source of income
· Lack of education
· Climate change
· Poor health
Little, or no source of income
Although those in poverty cannot afford to feed their families, research has proven that it is not because of a lack of food that people are poor – in fact, the world produces more than enough food to feed the entire world population. However international grain prices has been kept artificially high because the rich crop producing countries do not want to see the price of their produce lowered in order to maintain a healthy profit margin for their farm products. They would even go to the extent to destroy surplus crops rather than see the price go down. Hence the poorest families in the world need to spend a higher percentage of their income on food each year due to these inflated food prices .
Farmers in poor countries do not have the capital or the technical know-how to produce food more economically and efficiently as their counterparts in the rich nations. They are often squeezed by their own government who imposes fees and taxes to their produce, hence they receive less for their crops and yet had to pay higher prices for fertilizers, transportation and labour costs.
The market economy also plays a role in the existence of poverty, with competition rising so that prices and wages are lowered, meaning people earn less money until they cannot afford to buy goods, causing even more competition.
Lack of Education
One of the most important factors in the cause of poverty is a lack of education, preventing people from obtaining further education, and/or a job in the future, stopping them from earning a source of income. Although many children wish for education, many families are too poor to afford proper schooling, due to reasons such as an illness preventing them from earning money, or a lack of education which prevented them from getting a job.
Climate Change
Climate change is one of the biggest causes of poverty, putting precious resources at risk, increasing the chance of illnesses, and forcing people out of their homes and into neighbouring countries. Climate change acts as the catalyst for why many people end up in poverty, particularly in the sense of famine.
Poor Health
People in poverty cannot afford medical aid, so it is critical when somebody becomes ill. Poor health restricts movement and decreases the amount of work impoverished individuals can do, lowering their income and driving them even deeper into poverty.
The Cycle of Poverty + Original Model
The Cycle of Poverty
The cycle of poverty is when a family is stuck in poverty for generations, unable to get out due to personal factors such as lack of education, a poor income, and/or poor health. Often called the development trap, people are forever in the grasps of poverty, without critical resources, unless helped by outside intervention. An example of how people become trapped within this cycle is when a person has no money to afford food, and a good education. Without food, the person becomes malnourished, becoming ill and maybe even catching a disease. This person lacks the qualifications to get a job, and is not able to afford medical care, although, if too ill, may not be able to work at all. This continues in a cycle which is extremely difficult to escape.
Original Model
Abolishing poverty is no easy feat. To eradicate poverty, action must be taken to provide those in need with the basic everyday essentials; clean water, nutrition, a proper education, healthcare and sanitation, to name just a few. Special attention is required for different groups such as young children, the elderly and pregnant women, ensuring they receive the proper health care and financial assistance. Education should be made compulsory for every child, and more jobs be made available, to allow everybody an equal opportunity to have a source of income.
Possible Solutions
Education and health care
The economic function of education is to increase a person’s capacity to make a decent living for themselves, which is complemented by the political function; to strengthen their capacity to evaluate their leaders critically. Good education not only lays the basis for economic development, but also for a good government system. Also, education will allow individuals to qualify for a job, providing them with a source of income.
Healthcare is at least, if not more important than education, also crucial in making good use of a proper education. A well-developed system of healthcare is required in all countries, with proper aids to prevent diseases through vaccinations and health check-ups. Emphasis should be put on family planning and adequate nutrition essential for sustaining health. Also, clean water and sanitation should be provided to every family, as it is essential in preventing diseases and other illnesses.
Job creation
A lack of a job is one of the main reasons why people, once trapped in poverty, can never get out again. This can be for many reasons; namely the lack of qualifications, or, a lack of job availability. Job availability will grant people a source of income, and increase the amount of supply and demand of resources.
Birth Control + Family Planning
Families should be discouraged to have children if they are currently living on an income insufficient to provide for them and the child. This ensures that the unborn child will not suffer due to lack of money, and will not further increase the existence of poverty by population growth.
International Trade
Trade relations enable developing countries to sell their goods and services to other countries, creating more jobs and generating income for their citizens. However, due to the tariffs set in place by richer countries, the developing countries are unable to gain access to overseas markets due to these trade barriers. To counter this problem, richer countries should be encouraged to lower their tariffs in order to help promote better trading conditions for the poorer countries.
Many rich countries have introduced programmes to subsidise their own produces, making it even harder for developing countries to compete with them in the international market.
International Aid

Richer countries should donate a percentage of their GDP to developing countries, which will help build up their infrastructure. Already, for every $100 earned in the country, Australia is donating 30 cents (0.3% of income) for aid. Other countries donating include Norway, Sweden and Netherlands, all of whom have reached their pledged goal of donating at least 0.7% of their income for international aid.
Increasing Awarness
 Campaigns such as the UN's Stand Up events are designed to increase the awarness of society towards the importance of eradicating poverty. If we increase the awarness of poverty then people will be more likely to take action (donating money, volunteering, protesting, etc.)
Campaigns such as the UN's Stand Up events are designed to increase the awarness of society towards the importance of eradicating poverty. If we increase the awarness of poverty then people will be more likely to take action (donating money, volunteering, protesting, etc.)Analysing
Education and Health care
For everyone, education provides the qualifications needed to get the job of their choice, earning them income. Without an education, these qualifications will not be granted, and a job therefore inaccessible. Furthermore, without health care, individuals would not be able to work, lowering what income they possess, decreasing their chance of living a full, enjoyable life.
Job creation
Because there is a lack of jobs, as well as an individual’s lack of education, people are being stripped of the chance to earn money, therefore not being able to afford basic needs.
Birth Control + Family Planning
Everywhere in the world, it is proven that the poorest families have the most children, making them spend more money when it is not sufficient to look after the whole family. As a result, the children must work and suffer to help the family earn money, especially if the parent/s is/are ill and cannot work themselves.
International Trade
Because many developed countries heavily subsidies their own producers, undeveloped countries have a harder time selling their product in the international market. (The United States government provides heavy subsidies to their farm produce)
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are many ways to abolish poverty, although to completely eradicate it will take a lot of effort, and time. Help is needed not only from the government, but from every individual, to counter the world problem. Main solutions to poverty include compulsory education, healthcare, family planning and international trade.
Bibliography
Information
- Websites
http://library.thinkquest.org/25009/causes/causes.cycle.html
http://www.globalissues.org/issue/2/causes-of-poverty
http://www.globalissues.org/article/408/sustainable-development-introduction
http://home.wanadoo.nl/f.j.doorman/Page18.htm
http://www.care.org/campaigns/poverty.asp
http://www.worldvision.com.au/wvconnect/content.asp?topicID=132
http://library.thinkquest.org/05aug/00282/over_causes.htm
http://library.thinkquest.org/05aug/00282/other_glossary.htm#cycle
http://encyclopedia.farlex.com/Cycle+of+poverty
http://www.sustainabilityinstitute.org/dhm_archive/index.php?display_article=vn126manupured
http://www.poverty.com/internationalaid.html
http://www.standagainstpoverty.org/
- Books
“Issues in Society – World Poverty” Edited by Justin Healey. Published by The Spinney Press in 2006.
“World Issues – Poverty” by Kaye Stearman. Published by Belitha Press in 2002.
“Planet under Pressure – Poverty” by Paul Mason. Published by Harcot Education Ltd. in 2006.
Pictures
http://news.bbc.co.uk/nol/shared/spl/hi/pop_ups/03/world_beating_poverty0/img/4.jpg
http://www.undispatch.com/archives/stand%20up%20logo.jpg
http://www.bbc.co.uk/radio4/today/gallery/media/poverty2.jpg
http://www.solarnavigator.net/images/Poverty_percent_world_map.jpg
http://graphics8.nytimes.com/images/2007/07/12/world/12mideast.600.jpg

